|
|
| Untersuchte Arbeit: Seite: 13, Zeilen: 1-1 |
Quelle: Wright 2005 Seite(n): 59, Zeilen: figure |
|---|---|

Figure 2: Schematic structure of airway and alveolus and their host-defence mechanisms. The lung is constantly challenged by inhaled pathogens, pollutans [sic] and particles. Several different defence mechanisms contribute to lung defence. These include filtration in the naso-oropharynx and conducting airways, sneezing, coughing and mucociliary clearance. Small particles might reach the alveolar gas-exchange regions of the lung. Host-defence functions in the peripheral air-spaces include surfactant, other opsonins (such as immunoglobulins) and innate immune cells (including alveolar macrophages and neutrophiles [sic]). Surfactant protein A (SP-A); surfactant protein D (SP-D) (adapted from Wright, 2005). Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005 Jan; 5 (1): 58-68. Review. |
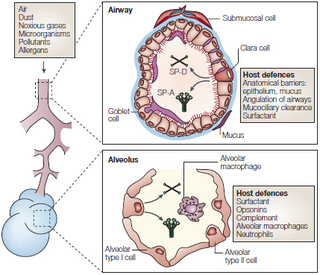
Figure 1 Lung host-defence mechanisms. The lung is constantly challenged by inhaled pathogens, pollutants and particles. Several different defence mechanisms contribute to lung defence. These include filtration in the naso-oropharynx and conducting airways, sneezing, coughing and mucociliary clearance. Small particles might reach the alveolar gas-exchange regions of the lung. Host-defence functions in the peripheral air-spaces include surfactant, other opsonins (such as immunoglobulins) and innate immune cells (including alveolar macrophages and neutrophils). SP-A, surfactant protein A; SP-D, surfactant protein D. |
The source is given, but it does not make clear that the extensive figure caption is copied literally from the source. Neither does the word "adapted" suggest that the figure is an exact copy of the figure in the source. |
|