|
|
| Untersuchte Arbeit: Seite: 2, Zeilen: 7-16 |
Quelle: Van Oostrom et al 2008 Seite(n): 1380, Zeilen: Figure 1, l.Sp. 13 ff. |
|---|---|
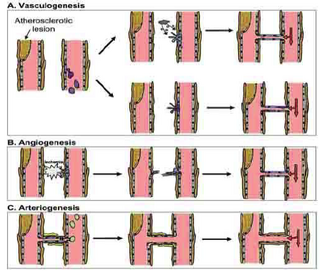
| Fig. 1.1.
[6] (Van Oostrom, M.C., et al., J Leukoc Biol, 2008;84(6): 1379-91) Fig.1.1. Neovascularization can occur via vasculogenesis (A), angiogenesis (B), or arteriogenesis (C). (A) In vasculogenesis, circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC; purple) contribute to new blood vessel growth (capillaries). (B) During angiogenesis, endothelial cells are activated by ischemia and develop a lumen, thereby forming a new, small capillary vessel[3]. (C) In arteriogenesis, circulating leukocytes (green) are attracted to the activated endothelium. They assist in enlarging collateral anastomoses. Activated endothelial cells (blue), activated vascular smooth muscle cells (yellow)[3]. Normally, there is only a minimal net flow in these pre-existing connections. However, a sudden arterial occlusion or a slow progressing stenosis in the main artery can cause an increased pressure gradient in these small vessels to respond by actively proliferating and remodeling, which results in an increased lumen size and enhanced [perfusion to the ischemic tissue[20]. Hence, it seems that arteriogenesis is initiated differently and progresses differently from angiogenesis.] 3. Carmeliet, P., Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med, 2000. 6(4): p. 389-95. 6. van Oostrom, M.C., et al., Insights into mechanisms behind arteriogenesis: what does the future hold? J Leukoc Biol, 2008. 84(6): p. 1379-91. 20. Schaper, W. and D. Scholz, Factors regulating arteriogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2003. 23(7): p. 1143-51. |
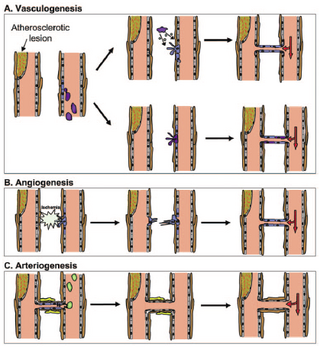
Fig. 1. Neovascularization can occur via vasculogenesis (A), angiogenesis (B), or arteriogenesis (C). (A) In vasculogenesis, circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC; purple) contribute to new blood vessel growth (capillaries) by secreting the necessary growth factors and chemokines for endothelial cells to migrate (upper) or by incorporating into the newly formed vessels (lower). (B) During angiogenesis, endothelial cells are activated by ischemia and grow in the direction of angiogenic signals. The endothelial cells fuse and develop a lumen, thereby forming a new, small capillary vessel. (C) In arteriogenesis, circulating leukocytes (green) are attracted to the activated endothelium. They assist in enlarging collateral anastomoses. Activated endothelial cells (blue), activated vascular smooth muscle cells (yellow), quiescent endothelial cells (gray), quiescent smooth muscle cells (brown). [...] Normally, as a result of the high resistance of arteriolar anastomoses and the lack of a pressure gradient, there is only a minimal net flow in these pre-existing connections. However, a sudden arterial occlusion or a slow progressing stenosis in the main artery can cause an increased pressure gradient in the anastomoses, leading to increased blood flow inside. These small vessels respond by actively proliferating and remodeling, which results in an increased lumen size and enhanced perfusion to the ischemic tissue [11]. Hence, it seems that arteriogenesis is initiated differently and progresses differently to angiogenesis. 11. Schaper, W., Scholz, D. (2003) Factors regulating arteriogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 1143–1151. |
Die Quelle ist für die Abbildung angegeben, nicht jedoch für die Bildunterschrift und den darauffolgenden Text. Auf die Bildunterschrift könnte man die Quellenangabe bei großzügiger Handhabung erstrecken, auf den Text schwerlich. |
|